What is Superfluid?
Introduction
Superfluid is a revolutionary asset streaming and distribution protocol bringing subscriptions, salaries, vesting, and rewards to DAOs and crypto-native businesses worldwide. This is made possible by the protocol’s smart contract framework which introduces the Super Token - an extension to the ERC-20 standard enabling the transfer of value in completely novel ways.
Super Tokens
The Superfluid protocol is a designed to be a "token-centric" protocol, in that all of its functionalities revolve around the concept of Super Tokens. The framework & Super Token standard can be used to add dynamic balances to tokens on chain, describing cash flows and executing them automatically over time in a non-interactive way. Any token can be transferred in Superfluid streams or distributions, which are programmable, composable, and modular. No capital is locked up, and all inflows and outflows are netted in real-time at every block without consuming any gas. The code is fully open source, while the protocol is non-custodial and permissionless.

A visualization of the Superfluid Protocol
The Superfluid Protocol has currently two main pillars that define its interactions with Super Tokens. These pillars (formerly called Agreements) are the following:
- Money Streaming - A set of features that enable the creation of money streams between two parties.
- Distributions - A set of features that enables the creation of a pool of funds that can be distributed to multiple recipients.
We go in further details about these two pillars in the next sections.
Money Streaming
Definition
Money Streaming is a continuous transfer of tokens from a sender to a receiver at a defined per-second rate, resulting in a "stream". This stream is perpetual and persists until it's canceled by either the sender or the receiver, or until the sender's Super Token balance is depleted.
Explanation
Money Streaming is a novel approach to token transfers, offering a dynamic way of sending funds. Instead of one-time transactions, tokens flow from the sender to the receiver continuously, creating a stream. This method provides real-time financial transactions, enabling a more fluid movement of assets over time, reflecting real-world economic activities more closely.
Example
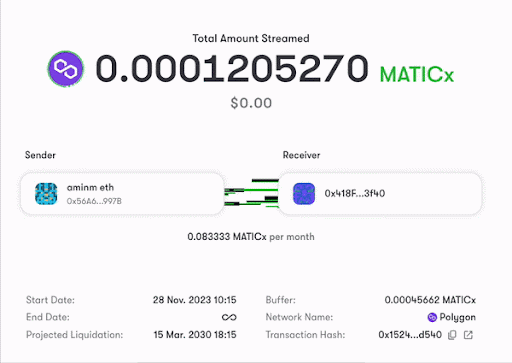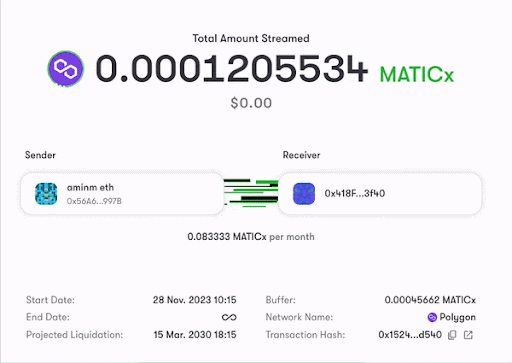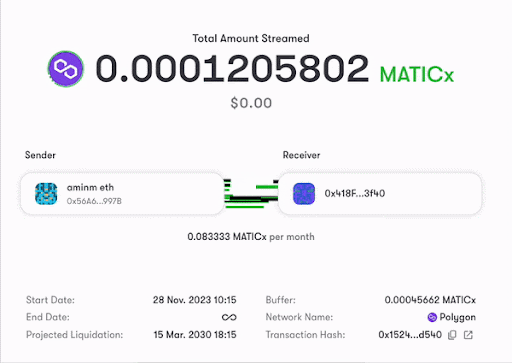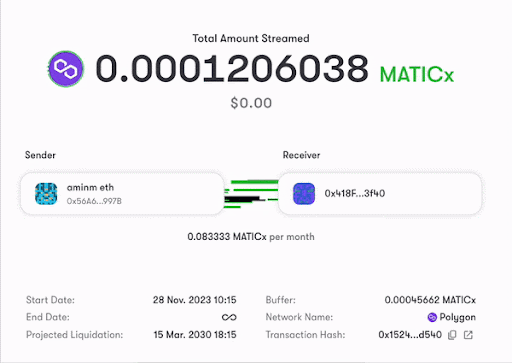
A visualization of money streaming from the Superfluid dashboard
Consider Alice wants to pay Bob a salary of 1200 USDCx per year using Money Streaming. She sets up a stream with a flow rate of 0.038 USDCx per second. Bob's balance starts increasing every second, and Alice's decreases, ensuring a steady transfer of salary.
Distributions
Definition
Distributions in Superfluid refer to a scalable one-to-many fund transfer method. It involves creating pools with a pool admin managing units for members, who can receive funds instantly or through continuous streaming.
Explanation
Distributions are a significant advancement in decentralized finance, enabling efficient and scalable fund transfers among multiple recipients. This method is especially useful for scenarios where funds need to be distributed among many parties, like dividends or rewards, ensuring equitable and automated distribution based on predefined units.
Example
Imagine a DeFi project creating a reward pool for liquidity providers. The project sets up a distribution pool with a total of 1000 units. If a liquidity provider has 100 units, they receive 10% of the total funds distributed through the pool, either instantly or as a continuous stream, depending on the distribution method.